Factors Influencing Stock Prices
Better stock price – Stock prices are a dynamic reflection of numerous interconnected factors, constantly shifting in response to both internal company developments and external macroeconomic forces. Understanding these influences is crucial for investors and companies alike to make informed decisions and navigate the complexities of the market.
Economic Indicators and Stock Prices
Economic indicators such as inflation and interest rates significantly impact stock prices. High inflation, eroding purchasing power, often leads to decreased consumer spending and corporate profits, resulting in lower stock valuations. Conversely, rising interest rates increase borrowing costs for businesses, potentially hindering investment and growth, thus negatively affecting stock prices. Conversely, low inflation and stable interest rates generally create a favorable environment for investment and economic expansion, boosting stock prices.
Company Performance and Stock Valuation
A company’s financial performance is a primary driver of its stock price. Strong earnings growth, indicating profitability and efficiency, typically leads to higher stock valuations. Revenue growth demonstrates market demand and expansion potential, further influencing investor confidence and stock prices. Conversely, declining earnings and revenue signal potential financial distress, prompting a decrease in stock price.
Achieving a better stock price often requires careful analysis and understanding of market trends. A key aspect of this involves monitoring specific companies, such as checking the current performance of the awp stock price , to gain insights into potential investment opportunities. By comparing various stocks and their trajectories, investors can make more informed decisions toward securing a better stock price for their portfolio.
Market Sentiment and Investor Psychology
Market sentiment, the overall feeling of investors toward the market, heavily influences stock price fluctuations. Optimism and confidence lead to buying, driving prices upward, while pessimism and fear trigger selling, causing price drops. Investor psychology, encompassing factors like herd behavior and emotional responses, can amplify these effects, leading to market volatility.
Industry Trends and Stock Prices
Key industry trends significantly impact specific company stock prices. Technological advancements, changing consumer preferences, and regulatory changes can all reshape industry landscapes, favoring some companies while negatively affecting others. For example, the rise of e-commerce significantly impacted brick-and-mortar retailers, leading to stock price declines for some while boosting others in the online retail sector.
Geopolitical Events and Stock Market Movements
Geopolitical events, such as international conflicts, political instability, and trade disputes, create uncertainty and volatility in the stock market. These events can significantly impact stock prices, often leading to sharp fluctuations depending on the perceived risk and impact on specific industries or global economies. The 2022 Russia-Ukraine war, for instance, significantly impacted energy and commodity markets, causing stock price volatility in related sectors.
Analyzing Company Financials for Stock Price Improvement Potential
Analyzing a company’s financial statements—the income statement, balance sheet, and cash flow statement—is essential for evaluating its financial health and predicting its future stock price performance. A thorough analysis allows investors to identify potential for improvement and assess the company’s long-term viability.
Interpreting the Income Statement
The income statement shows a company’s revenues, expenses, and profits over a period. Analyzing key metrics like revenue growth, gross profit margin, and net income helps assess profitability and operational efficiency. A step-by-step approach involves examining each line item, calculating key ratios, and comparing them to industry benchmarks and historical trends.
Assessing Balance Sheet Strength
The balance sheet provides a snapshot of a company’s assets, liabilities, and equity at a specific point in time. Analyzing metrics like the current ratio (liquidity), debt-to-equity ratio (leverage), and working capital helps assess the company’s financial stability and its ability to meet its obligations. A strong balance sheet indicates a lower risk profile and increased potential for stock price appreciation.
Evaluating the Cash Flow Statement
The cash flow statement tracks the movement of cash into and out of a company. Analyzing operating cash flow, investing cash flow, and financing cash flow helps predict future performance and financial flexibility. A consistent positive operating cash flow suggests strong profitability and sustainable growth, which is usually reflected in a higher stock price.
Key Financial Ratios and Stock Price Implications
Several key financial ratios provide insights into a company’s financial health and its potential for stock price improvement. The Price-to-Earnings (P/E) ratio indicates market valuation relative to earnings, while the debt-to-equity ratio shows the proportion of debt financing. Analyzing these ratios in conjunction with other financial metrics helps investors determine a company’s intrinsic value and potential for growth.
Financial Modeling and Stock Price Projection
Financial modeling involves creating projections of future financial performance based on different scenarios. This helps investors assess the potential impact of various factors on stock price. For example, a model could project future stock price based on different revenue growth rates, profit margins, and discount rates. This provides a range of potential outcomes, informing investment decisions.
Strategies for Improving a Company’s Stock Price
Companies can employ various strategies to enhance their stock price. These strategies focus on improving financial performance, enhancing investor relations, and optimizing capital structure.
Increasing Revenue and Profitability
Strategies to boost revenue and profitability include expanding into new markets, launching innovative products or services, improving operational efficiency, and implementing effective pricing strategies. For example, a company might invest in research and development to create new products with higher profit margins, or explore new geographical markets to reach a wider customer base.
Cost Reduction and Efficiency Improvements
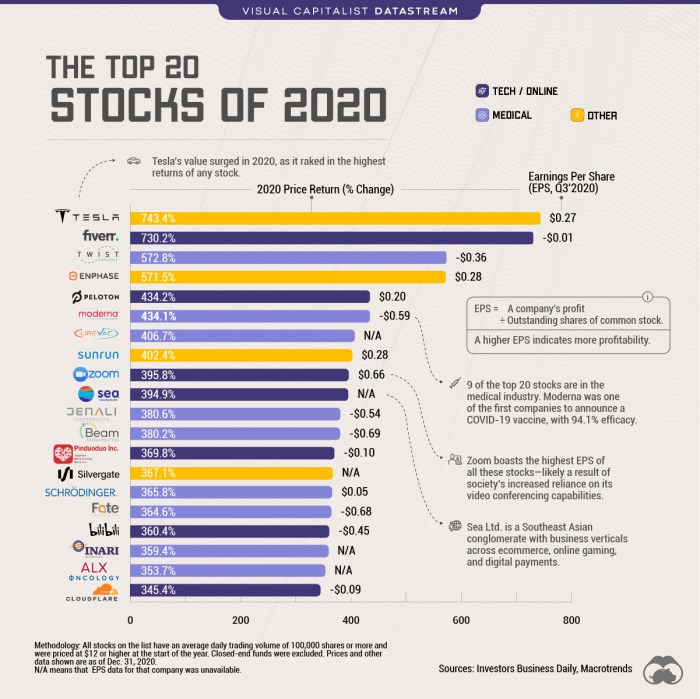
Source: visualcapitalist.com
Cost reduction and efficiency improvements are crucial for enhancing profitability and boosting stock prices. Strategies include streamlining operations, optimizing supply chains, reducing waste, and leveraging technology to automate processes. Lean manufacturing principles and Six Sigma methodologies are commonly used to achieve these improvements.
Mergers and Acquisitions
Mergers and acquisitions can enhance stock value by creating synergies, expanding market share, and accessing new technologies or resources. However, successful integration is crucial, as poorly managed mergers can negatively impact stock prices. A thorough due diligence process and a clear integration plan are essential for maximizing the benefits of M&A activities.
Share Buyback Programs
Share buyback programs involve a company repurchasing its own shares, reducing the number of outstanding shares and potentially increasing earnings per share (EPS). This can lead to higher stock prices, but it’s crucial to consider the opportunity cost of using capital for buybacks instead of other potentially more valuable investments.
Improving Investor Relations and Communication
Effective investor relations and communication are essential for building trust and transparency with investors. Regularly providing clear and concise financial reports, actively engaging with analysts and investors, and maintaining a strong corporate reputation are crucial for fostering investor confidence and improving stock price.
Market Conditions and Their Effect on Stock Prices
Market conditions significantly influence stock prices. Understanding market cycles, volatility, and macroeconomic policies is crucial for navigating the market effectively.
Market Cycles and Stock Prices
Bull markets, characterized by rising prices and investor optimism, typically lead to stock price increases. Conversely, bear markets, characterized by falling prices and investor pessimism, result in stock price declines. Understanding the phase of the market cycle is essential for adjusting investment strategies.
Asset Class Performance During Market Conditions, Better stock price
Different asset classes perform differently during various market conditions. For example, bonds often perform well during bear markets as investors seek safer investments, while growth stocks tend to outperform during bull markets. Diversification across asset classes helps mitigate risk during market downturns.
Market Volatility and Stock Prices
Market volatility, measured by the fluctuation of prices, can significantly impact stock prices. High volatility creates uncertainty and risk, leading to price swings. Factors contributing to volatility include economic uncertainty, geopolitical events, and investor sentiment. Understanding volatility helps investors manage risk and adjust their investment strategies accordingly.
Macroeconomic Policies and Stock Prices
Macroeconomic policies, such as monetary policy (interest rates) and fiscal policy (government spending), significantly impact stock prices. Expansionary monetary policies, for instance, often lead to lower interest rates and increased investment, boosting stock prices. Conversely, contractionary policies can have the opposite effect.
Market Regulation and Stock Price Stability
Market regulation plays a vital role in ensuring stock price stability and protecting investors. Regulations aim to prevent market manipulation, ensure transparency, and promote fair trading practices. Changes in regulations can have both positive and negative impacts on specific stock sectors.
| Regulatory Change | Affected Sector | Impact on Stock Prices | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Increased environmental regulations | Energy | Potentially negative for fossil fuel companies, positive for renewable energy companies | Increased carbon emission standards leading to higher costs for coal power plants. |
| New data privacy regulations | Technology | Potentially negative for companies with weak data security practices, positive for companies with strong data security | GDPR implementation impacting the stock prices of companies failing to comply. |
| Deregulation of a specific industry | Financial Services | Potentially positive for companies in that sector, potentially increased volatility | Easing of banking regulations potentially leading to higher profits but also higher risk for banks. |
| Increased financial reporting requirements | All Sectors | Potentially negative in the short-term due to increased compliance costs, potentially positive in the long-term due to increased transparency | Stricter accounting standards potentially increasing compliance costs but leading to greater investor confidence. |
Long-Term vs. Short-Term Stock Price Growth
Investors can choose between long-term investment strategies and short-term trading approaches, each with distinct risk and reward profiles. Understanding these differences is crucial for aligning investment strategies with personal financial goals and risk tolerance.
Long-Term vs. Short-Term Investment Strategies
Long-term investment strategies focus on holding stocks for extended periods, typically years or even decades, aiming to benefit from long-term growth and compounding returns. Short-term trading involves buying and selling stocks frequently, aiming to profit from short-term price fluctuations. Long-term strategies generally involve lower risk but potentially slower returns, while short-term trading involves higher risk but the potential for faster, though potentially smaller, gains.
Risks and Rewards of Investment Timeframes
Long-term investing carries lower risk due to the time horizon allowing for market fluctuations to even out. However, returns may be slower. Short-term trading carries higher risk due to market volatility and the potential for quick losses. However, the potential for quick profits exists as well. Careful risk management is essential for both approaches.
Importance of Diversification in Managing Investment Risk
Source: speedtrader.com
Diversification is crucial for managing investment risk, regardless of the timeframe. Spreading investments across different stocks, sectors, and asset classes reduces the impact of losses in any single investment. A well-diversified portfolio reduces overall portfolio volatility and improves risk-adjusted returns.
Examples of Companies Suitable for Different Timeframes
Companies with strong long-term growth potential, such as those in innovative technology sectors or with sustainable competitive advantages, are suitable for long-term investments. Companies with high volatility and frequent price swings, often in speculative sectors, might be suitable for short-term trading. However, careful analysis is crucial for any investment decision.
Risk and Reward Profiles for Long-Term vs. Short-Term Investments
A visual representation would show a long-term investment profile as a relatively gentle upward sloping curve with lower volatility, illustrating lower risk and potentially slower, steadier returns. A short-term investment profile would be a much steeper, more volatile curve with sharper peaks and troughs, representing higher risk and the potential for both higher gains and losses.
FAQ Guide: Better Stock Price
What is the role of dividends in influencing stock price?
Dividends can positively influence stock price by attracting income-seeking investors. However, the impact depends on factors like dividend yield and the overall market environment.
How do short-selling and margin trading affect stock prices?
Short-selling and margin trading can increase market volatility and contribute to both price increases and decreases, depending on the prevailing market sentiment and investor behavior.
What is the impact of regulatory changes on specific sectors?
Regulatory changes can significantly impact stock prices within specific sectors. For example, stricter environmental regulations might negatively affect energy companies, while new healthcare regulations could impact pharmaceutical firms. The effect is highly sector-specific.